Cloud network security solutions are essential for protecting your organization’s data and applications in the cloud. With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, it’s more important than ever to have a robust cloud security strategy in place.
This guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of cloud network security, including the latest trends, best practices, and tools. We’ll cover everything from cloud network architecture to cloud incident response, so you can be sure that your cloud environment is secure.
Cloud Network Security Architecture
Cloud network security architecture forms the foundation for protecting cloud-based networks and data. It involves implementing security controls and measures to safeguard virtual networks, workloads, and network traffic.
A robust cloud network security architecture is characterized by:
- Defense-in-Depth Approach:Employing multiple layers of security controls to mitigate risks and prevent single points of failure.
- Zero Trust Model:Assuming all network traffic is untrusted and requiring authentication and authorization for every access attempt.
- Segmentation and Isolation:Dividing the network into smaller segments to limit the spread of threats and isolate critical assets.
Cloud Network Security Components
Key components of a cloud network security architecture include:
- Virtual Firewalls:Enforcing security policies and filtering network traffic based on defined rules.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS):Monitoring network traffic for suspicious activities and taking appropriate actions.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAFs):Protecting web applications from vulnerabilities and attacks.
- Network Access Control (NAC):Controlling access to the network based on device and user identity.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM):Monitoring and managing cloud security configurations to ensure compliance and reduce risks.
Best Practices for Designing a Secure Cloud Network Architecture
When designing a cloud network security architecture, consider the following best practices:
- Establish a Clear Security Policy:Define security goals, roles, and responsibilities to guide architecture design and implementation.
- Adopt a Defense-in-Depth Approach:Implement multiple layers of security controls, including firewalls, intrusion detection, and segmentation.
- Use Cloud-Native Security Services:Leverage cloud-based security services that are designed to protect cloud environments.
- Implement Identity and Access Management (IAM):Control access to cloud resources based on user identity and authorization.
- Monitor and Audit Regularly:Continuously monitor network activity and audit security configurations to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Cloud Network Segmentation: Cloud Network Security Solutions

Network segmentation is a critical security measure that can help you to protect your cloud-based resources from unauthorized access. By dividing your network into smaller, isolated segments, you can limit the potential impact of a security breach.There are many benefits to implementing network segmentation in the cloud, including:*
-*Improved security
Network segmentation can help to prevent unauthorized access to your cloud-based resources by limiting the number of potential attack vectors.
-
- -*Reduced risk of data breaches By isolating different parts of your network, you can reduce the risk of a data breach spreading to other parts of your infrastructure.
-*Improved performance
Network segmentation can help to improve the performance of your cloud-based applications by reducing network congestion.
-*Easier management
Network segmentation can make it easier to manage your cloud-based infrastructure by providing a more logical and organized structure.
However, there are also some challenges to implementing network segmentation in the cloud, including:*
-*Complexity
Network segmentation can be a complex and time-consuming process to implement.
-
- -*Cost Network segmentation can add to the cost of your cloud-based infrastructure.
-*Operational overhead
Network segmentation can increase the operational overhead of your cloud-based infrastructure.
Despite these challenges, network segmentation is a valuable security measure that can help you to protect your cloud-based resources from unauthorized access.There are several different methods for implementing network segmentation in the cloud, including:*
-*Virtual LANs (VLANs)
VLANs are a logical way to segment your network into different segments. VLANs are created using software and can be used to segment your network by department, function, or security level.
-
- -*Security groups Security groups are a way to segment your network by IP address or port. Security groups can be used to control access to specific resources on your network.
-*Network access control lists (ACLs)
ACLs are a way to control access to your network by IP address or port. ACLs can be used to deny or allow access to specific resources on your network.
The best method for implementing network segmentation in the cloud will depend on your specific needs and requirements.Here are some examples of effective network segmentation strategies:*
-*Segment your network by department
This can help to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data by limiting the number of people who have access to it.
-
- -*Segment your network by function This can help to improve the performance of your cloud-based applications by reducing network congestion.
-*Segment your network by security level
This can help to protect your most sensitive data from unauthorized access by isolating it from other parts of your network.
Here is a table summarizing the different methods for implementing network segmentation in the cloud, including their advantages and disadvantages:| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages ||—|—|—|| VLANs | Logical segmentation | Can be complex to configure || Security groups | Easy to configure | Can be less granular than VLANs || ACLs | Granular control | Can be complex to manage |Here are some best practices for implementing network segmentation in the cloud:*
-*Use a consistent segmentation strategy
This will help to make it easier to manage your network and reduce the risk of security breaches.
-
- -*Use a combination of segmentation methods This will provide you with the most flexibility and control over your network.
-*Monitor your network traffic
This will help you to identify any suspicious activity and take appropriate action.
-*Regularly review and update your segmentation strategy
This will help to ensure that your network is always protected from the latest threats.
Here is a real-world example of a company that has successfully implemented network segmentation in the cloud:*
-*Company
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
-*Solution
AWS uses a combination of VLANs, security groups, and ACLs to segment its network. This has helped AWS to improve the security and performance of its cloud-based services.
Cloud Firewall Management
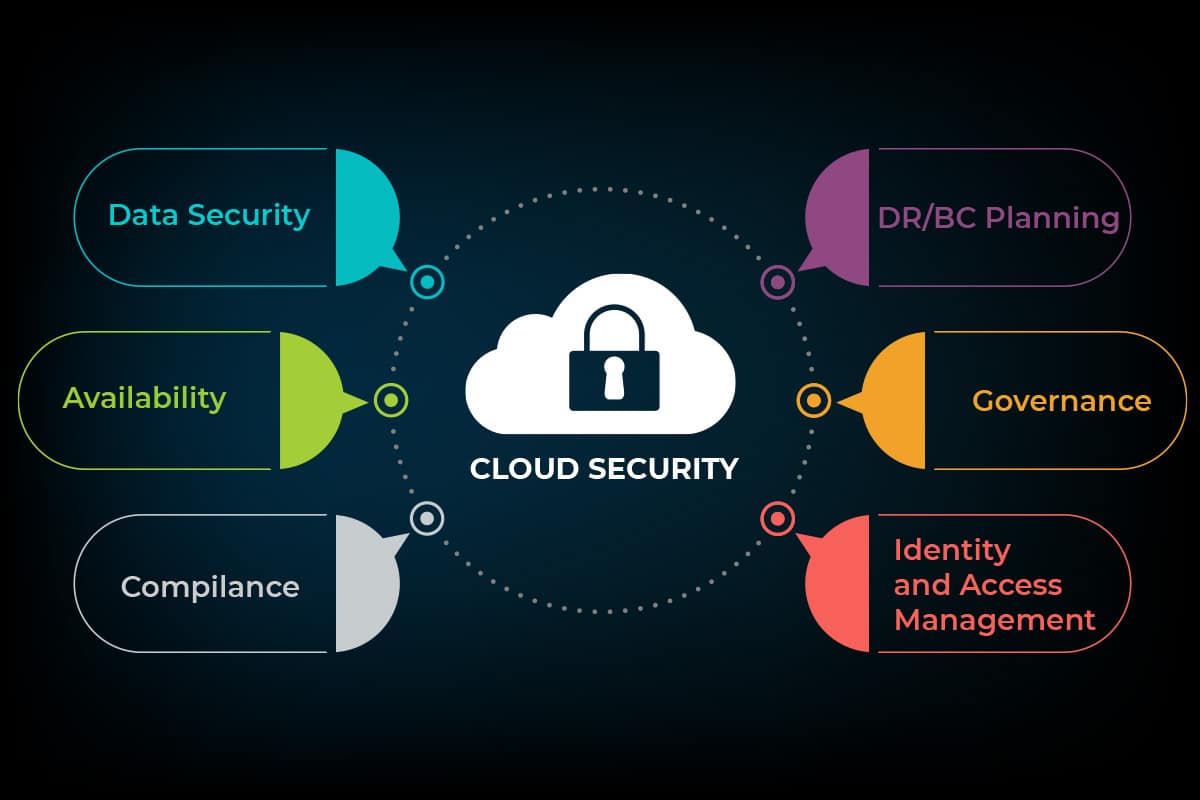
Cloud firewall management plays a pivotal role in safeguarding your cloud infrastructure from malicious actors and security threats. Effective firewall management enables you to monitor, control, and adjust network traffic, ensuring that only authorized traffic enters and exits your cloud environment.
Types of Cloud Firewalls
Cloud firewalls come in various types, each offering unique features and capabilities:
- Stateful Firewalls:Track the state of network connections, allowing or denying traffic based on previous interactions.
- Stateless Firewalls:Inspect individual packets independently, without regard to connection history.
- Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs):Advanced firewalls that provide deep packet inspection, intrusion detection, and prevention capabilities.
Configuring and Managing Cloud Firewalls, Cloud network security solutions
To ensure optimal security, it is crucial to configure and manage cloud firewalls effectively. Here are some best practices:
- Define Clear Firewall Policies:Establish comprehensive firewall rules that specify which traffic to allow or deny, based on source, destination, port, and protocol.
- Enable Logging and Monitoring:Regularly review firewall logs to identify suspicious activity and potential security breaches.
- Implement Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS):Detect and block malicious traffic in real-time.
- Use Cloud Security Management Tools:Leverage cloud-based security platforms that provide centralized visibility, management, and automation for your firewalls.
By adhering to these best practices, you can strengthen your cloud network security and protect your data and applications from unauthorized access.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) are essential components of a comprehensive cloud network security strategy. They monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, detect potential threats, and take action to prevent or mitigate attacks. IDPS can significantly enhance the security posture of cloud environments, reducing the risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and other malicious activities.
Types of IDPS
There are two main types of IDPS:*
-*Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS)
Monitor network traffic in real-time, analyzing packets for suspicious patterns and signatures.
-*Host Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS)
Monitor individual hosts or endpoints, detecting suspicious activities within the operating system, applications, and user behavior.
Deployment and Management in the Cloud
Deploying and managing IDPS in the cloud requires careful planning and configuration. Cloud providers typically offer managed IDPS services, simplifying deployment and maintenance. Alternatively, organizations can deploy their own IDPS appliances or virtual machines in the cloud.To ensure effective operation, IDPS should be properly configured with relevant threat signatures, rules, and policies.
Regular updates and maintenance are crucial to keep the system up-to-date with the latest threats and vulnerabilities.
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) are security solutions deployed in front of web applications to protect them from malicious traffic and attacks. WAFs act as a shield, inspecting and filtering incoming web traffic to identify and block malicious requests, while allowing legitimate traffic to pass through.
WAFs provide numerous benefits for cloud-based applications, including:
- Protection against common web application attacks such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and denial of service (DoS) attacks.
- Compliance with industry regulations and standards, such as PCI DSS and HIPAA.
- Improved application performance and availability by blocking malicious traffic before it reaches the application.
Types of WAFs
There are three main types of WAFs:
- Host-based WAFs: These WAFs are installed directly on the web server or application host. They monitor and filter traffic at the application level.
- Network-based WAFs: These WAFs are deployed at the network level, typically in front of the web server or application. They monitor and filter traffic at the network layer.
- Cloud-based WAFs: These WAFs are deployed as a service in the cloud. They provide centralized protection for multiple applications and can be easily scaled to meet changing traffic demands.
Deployment and Management of WAFs
Effective deployment and management of WAFs require careful planning and configuration. Best practices include:
- Configuration best practices: Configure WAFs to block common attack patterns and vulnerabilities, while allowing legitimate traffic to pass through.
- Monitoring and logging: Monitor WAF logs to identify and investigate security incidents and trends.
- Integration with other security tools: Integrate WAFs with other security tools, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) systems, to provide comprehensive protection.
Latest Trends and Advancements in WAF Technology
WAF technology is constantly evolving to keep pace with emerging threats and attack vectors. Some of the latest trends and advancements include:
- Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI): WAFs are increasingly using machine learning and AI to detect and block sophisticated attacks.
- Cloud-native WAFs: WAFs designed specifically for cloud environments, offering scalability, elasticity, and integration with cloud services.
- Managed WAF services: WAFs provided as a managed service, reducing the burden of deployment and management for organizations.
Cloud Access Control
Cloud access control is crucial for securing cloud environments by ensuring only authorized individuals and entities have access to cloud resources. It helps prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance violations.Different methods for implementing access control in the cloud include:
Role-based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC assigns permissions to users based on their roles within the organization. Each role has a predefined set of permissions that determine the resources and operations users can access.
Attribute-based Access Control (ABAC)
ABAC grants access based on attributes associated with users, resources, and the request context. Attributes can include factors like job title, location, device type, and time of day.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM is a cloud-based service that provides centralized management of access control across multiple cloud resources. It allows administrators to define and enforce access policies, manage user identities, and audit access logs.Effective cloud access control strategies include:
-
- -*Using least privilege Granting users only the minimum permissions necessary to perform their job functions.
-*Implementing multi-factor authentication
Requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing sensitive resources.
-*Regularly reviewing and auditing access permissions
Monitoring access logs and revoking unused or excessive permissions.
| Access Control Method | Advantages | Disadvantages ||—|—|—|| RBAC | Simple to implement and manage | Can be inflexible for complex organizations || ABAC | More granular control | Can be complex to configure and manage || IAM | Centralized management and visibility | May require additional setup and configuration |
Cloud access control is the foundation of cloud security. It ensures that only the right people have access to the right resources at the right time.”
Implementing cloud access control in a multi-cloud environment can be challenging due to the need to manage access across multiple cloud providers with different security policies and tools. This requires a comprehensive approach that involves integrating access control systems, establishing consistent policies, and monitoring access logs across all cloud environments.
Cloud Security Monitoring
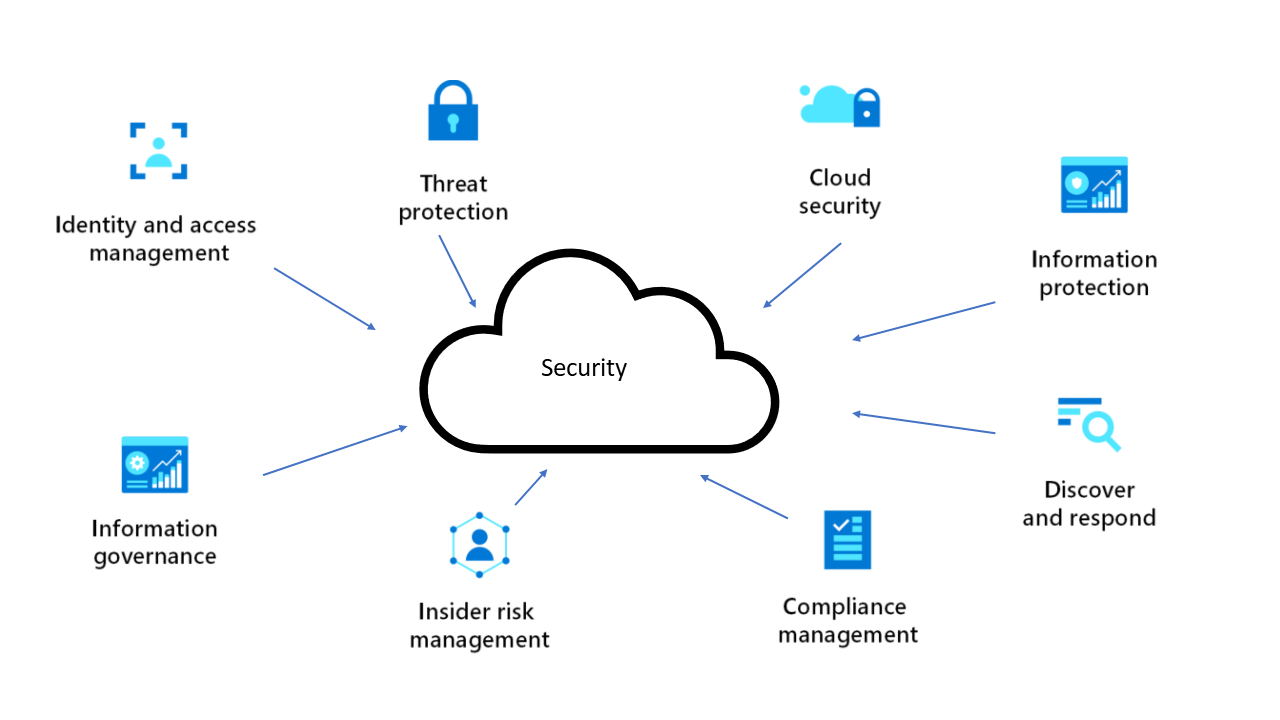
Cloud security monitoring is the practice of continuously monitoring and analyzing cloud environments to detect and respond to security threats. It involves collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data from various sources, such as cloud logs, metrics, and security events, to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities.
Cloud security monitoring tools provide a range of features to help organizations protect their cloud environments, including:
- Log analysis:Monitoring cloud logs for suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access attempts or data breaches.
- Metric analysis:Monitoring cloud metrics, such as CPU usage and network traffic, for anomalies that may indicate a security incident.
- Security event monitoring:Monitoring security events, such as firewall alerts or intrusion detection alerts, to identify potential threats.
- Vulnerability scanning:Scanning cloud resources for vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
- Threat intelligence:Integrating with threat intelligence feeds to stay informed about the latest security threats and vulnerabilities.
Implementing a comprehensive cloud security monitoring strategy is essential for organizations to protect their cloud environments from security threats. This involves:
- Identifying critical assets:Identifying the most critical assets in the cloud environment and prioritizing their protection.
- Selecting the right monitoring tools:Choosing cloud security monitoring tools that meet the specific needs of the organization.
- Establishing baselines:Establishing baselines for normal activity in the cloud environment to help identify anomalies.
- Setting up alerts:Configuring alerts to notify the security team of potential security threats.
- Integrating with other security solutions:Integrating cloud security monitoring tools with other security solutions, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, to provide a comprehensive security posture.
Cloud Incident Response: Importance and Benefits
Cloud incident response is crucial for safeguarding cloud environments and mitigating the impact of security breaches. It involves a systematic approach to detect, contain, mitigate, recover from, and learn from security incidents.
Effective cloud incident response plans provide numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced downtime and data loss
- Improved compliance with regulatory requirements
- Enhanced customer trust and reputation
- Lower insurance premiums and legal costs
Steps Involved in Cloud Incident Response
Cloud incident response typically involves the following steps:
Detection and Analysis
Identifying and analyzing security incidents through monitoring tools, threat intelligence, and security logs.
Containment and Mitigation
Isolating affected systems, implementing countermeasures, and containing the spread of the incident.
Recovery and Post-Incident Review
Restoring affected systems and services, conducting a thorough post-incident review to identify root causes and improve response strategies.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Cloud network security is subject to various compliance and regulatory requirements, depending on the industry and jurisdiction. Understanding and adhering to these requirements is crucial for businesses to ensure the protection of sensitive data, avoid legal penalties, and maintain customer trust.
To align cloud network security measures with industry standards, organizations should:
- Identify applicable compliance and regulatory requirements based on their industry, location, and data sensitivity.
- Review and understand the specific security controls and measures required by each regulation.
- Implement and maintain appropriate cloud network security controls to meet the requirements.
Meeting Specific Compliance Requirements
Specific compliance requirements, such as PCI DSS or HIPAA, have their own unique security standards. To meet these requirements, organizations should:
- PCI DSS:Implement security measures to protect payment card data, including encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments.
- HIPAA:Establish and maintain appropriate safeguards to protect patient health information, including physical security measures, access controls, and data encryption.
By aligning cloud network security measures with industry standards and meeting specific compliance requirements, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to data protection and regulatory compliance, mitigating risks and enhancing their overall security posture.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Network Security
The cloud computing landscape is constantly evolving, and with it, the threats to cloud security. To stay ahead of these threats, it is important to be aware of the emerging trends in cloud network security.
One of the most significant trends is the increasing adoption of software-defined networking (SDN). SDN gives network administrators greater control over their networks, making it easier to implement security measures. SDN can also be used to automate security tasks, such as threat detection and response.
Another trend is the growing use of artificial intelligence (AI) in cloud security. AI can be used to detect and respond to threats in real time. AI can also be used to analyze security data and identify trends that can help to prevent future attacks.
Finally, the cloud is becoming increasingly integrated with other technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and edge computing. This convergence is creating new security challenges that need to be addressed.
Implications for Cloud Security Professionals
These emerging trends have a number of implications for cloud security professionals. First, they need to be aware of the new technologies and techniques that are being used by attackers. Second, they need to be able to implement and manage security measures that are effective against these new threats.
Third, they need to be able to work with other IT professionals to ensure that the cloud is integrated securely with other technologies.
Innovative Cloud Network Security Solutions
A number of innovative cloud network security solutions are available to help organizations protect their cloud environments. These solutions include:
- Software-defined networking (SDN)
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
- Cloud access security brokers (CASBs)
- Web application firewalls (WAFs)
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPSs)
By implementing these solutions, organizations can significantly improve their cloud security posture.
Case Studies and Best Practices
The effective implementation of cloud network security solutions has led to significant advancements in various industries. Let’s explore real-world case studies and delve into best practices that have contributed to these successes.
Cloud network security is a crucial aspect of securing cloud-based infrastructure and applications. Implementing effective security measures helps organizations protect their sensitive data, comply with regulations, and maintain business continuity.
Network Segmentation and Isolation
Network segmentation divides a network into smaller, isolated segments, limiting the spread of threats and data breaches. Best practices include:
- Implementing virtual LANs (VLANs) or network security groups (NSGs) to create logical network segments.
- Restricting access between segments using access control lists (ACLs) or firewall rules.
- Isolating critical systems and data from less sensitive resources.
Identity and Access Management
Identity and access management (IAM) controls user access to cloud resources. Best practices involve:
- Implementing strong authentication mechanisms like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO).
- Defining clear user roles and permissions based on the principle of least privilege.
- Regularly reviewing and auditing user access to identify and revoke unnecessary permissions.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention
Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) monitor network traffic for suspicious activities. Best practices include:
- Deploying IDPS sensors at strategic network points to detect and block malicious traffic.
- Using threat intelligence feeds to update IDPS rules and stay ahead of evolving threats.
- Integrating IDPS with other security tools for a comprehensive defense strategy.
Threat Intelligence and Monitoring
Threat intelligence and monitoring provide valuable insights into potential threats and vulnerabilities. Best practices encompass:
- Subscribing to threat intelligence feeds from reputable sources.
- Using security information and event management (SIEM) tools to collect and analyze security logs.
- Establishing a process for incident detection, investigation, and response.
Cloud Network Security Tools
Cloud network security tools are essential for protecting your organization’s data and applications in the cloud. These tools provide a variety of features to help you secure your network, including firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), virtual private networks (VPNs), web application firewalls (WAFs), and cloud access security brokers (CASBs).
There are a number of different cloud network security tools available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. It’s important to choose the right tool for your organization’s needs. To help you make an informed decision, we’ve compiled a table comparing different cloud network security tools.
Tool Comparison
| Tool | Vendor | Features | Pricing | Customer Reviews | Firewall | IDS/IPS | VPN | WAF | CASB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWS Network Firewall | Amazon Web Services | – Firewall IDS/IPS VPN WAF | – Pay-as-you-go pricing Starts at $0.025 per hour | – Positive customer reviews Praised for its ease of use and scalability | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Azure Firewall | Microsoft | – Firewall IDS/IPS VPN WAF | – Pay-as-you-go pricing Starts at $0.021 per hour | – Positive customer reviews Praised for its performance and reliability | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Google Cloud Firewall | Google Cloud | – Firewall IDS/IPS VPN WAF | – Pay-as-you-go pricing Starts at $0.02 per hour | – Positive customer reviews Praised for its flexibility and scalability | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Palo Alto Networks VM-Series | Palo Alto Networks | – Firewall IDS/IPS VPN WAF CASB | – Subscription pricing Starts at $1,500 per year | – Positive customer reviews Praised for its comprehensive security features | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Check Point CloudGuard | Check Point Software Technologies | – Firewall IDS/IPS VPN WAF CASB | – Subscription pricing Starts at $2,000 per year | – Positive customer reviews Praised for its advanced security features | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Cloud Network Security Tools
There are a number of advantages to using cloud network security tools, including:
- Improved security: Cloud network security tools can help you to protect your organization’s data and applications from a variety of threats, including malware, phishing attacks, and DDoS attacks.
- Reduced costs: Cloud network security tools can help you to reduce the cost of securing your network by eliminating the need for on-premises hardware and software.
- Increased flexibility: Cloud network security tools can be easily scaled up or down to meet the changing needs of your organization.
- Scalability: Cloud network security tools can be scaled to meet the needs of any size organization.
However, there are also some disadvantages to using cloud network security tools, including:
- Complexity: Cloud network security tools can be complex to configure and manage.
- Vendor lock-in: Cloud network security tools can lock you into a specific vendor, making it difficult to switch providers.
- Performance issues: Cloud network security tools can sometimes impact the performance of your network.
Choosing the Right Cloud Network Security Tool
When choosing a cloud network security tool, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- The size and complexity of your network
- The threats that you are most concerned about
- Your budget
- Your technical expertise
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the right cloud network security tool to meet the needs of your organization.
Cloud Network Security Whitepapers
Stay ahead of the curve in cloud network security with our curated list of whitepapers. These comprehensive resources provide valuable insights and actionable recommendations to help you safeguard your cloud infrastructure.
Whitepaper Library
- Cloud Network Security Best Practices This whitepaper Artikels essential best practices for securing your cloud network, including network segmentation, access control, and threat detection. Read Full Whitepaper
- Implementing a Zero Trust Network Architecture for Cloud Environments Discover the principles and benefits of implementing a Zero Trust Network Architecture (ZTNA) to enhance the security of your cloud network. Read Full Whitepaper
- Cloud Security Monitoring and Incident Response Learn how to effectively monitor your cloud network for security threats and respond promptly to incidents to minimize impact. Read Full Whitepaper
- Cloud Compliance and Regulatory Considerations Stay informed about the latest compliance and regulatory requirements for cloud network security and how to meet them. Read Full Whitepaper
- Emerging Trends in Cloud Network Security Explore the latest advancements and emerging trends in cloud network security to stay ahead of evolving threats. Read Full Whitepaper
Key Takeaways
By reading these whitepapers, you will gain a deeper understanding of:
- Best practices for securing cloud networks
- Benefits of implementing ZTNA
- Techniques for monitoring and responding to security incidents
- Compliance and regulatory requirements for cloud security
- Emerging trends and advancements in cloud network security
Cloud Network Security Glossary
Understanding the terminology associated with cloud network security is essential for effective implementation and management. Here’s a comprehensive glossary of key terms:
Access Control
- Authorization:The process of determining whether a user or entity is allowed to access a resource.
- Authentication:The process of verifying the identity of a user or entity.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM):A framework for managing user identities, roles, and access privileges.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
- Cloud Security Posture:The overall security state of a cloud environment, including its configuration, vulnerabilities, and compliance.
- CSPM Tools:Automated tools that monitor and assess cloud security posture, identify risks, and enforce compliance.
Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)
- Workload:A running application or service in the cloud.
- CWPP:A comprehensive security solution that protects workloads from threats, such as malware, intrusion attempts, and data breaches.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
- Intrusion Detection:Identifying unauthorized access or malicious activity on a network.
- Intrusion Prevention:Blocking or mitigating identified threats before they can cause damage.
Network Segmentation
- Virtual LAN (VLAN):A logical network segment that isolates traffic based on specific criteria, such as department or function.
- Micro-segmentation:A more granular approach to network segmentation, creating highly isolated network segments for individual workloads.
Threat Intelligence
- Threat Actor:An individual or group responsible for malicious activity.
- Threat Indicator:Information that can help identify or predict threats, such as IP addresses, URLs, or malware signatures.
- Threat Intelligence Feed:A collection of threat indicators that are shared among security professionals.
Final Summary
Cloud network security is a complex and ever-evolving field, but it’s essential for protecting your organization’s data and applications. By following the best practices and using the right tools, you can ensure that your cloud environment is secure and compliant.









